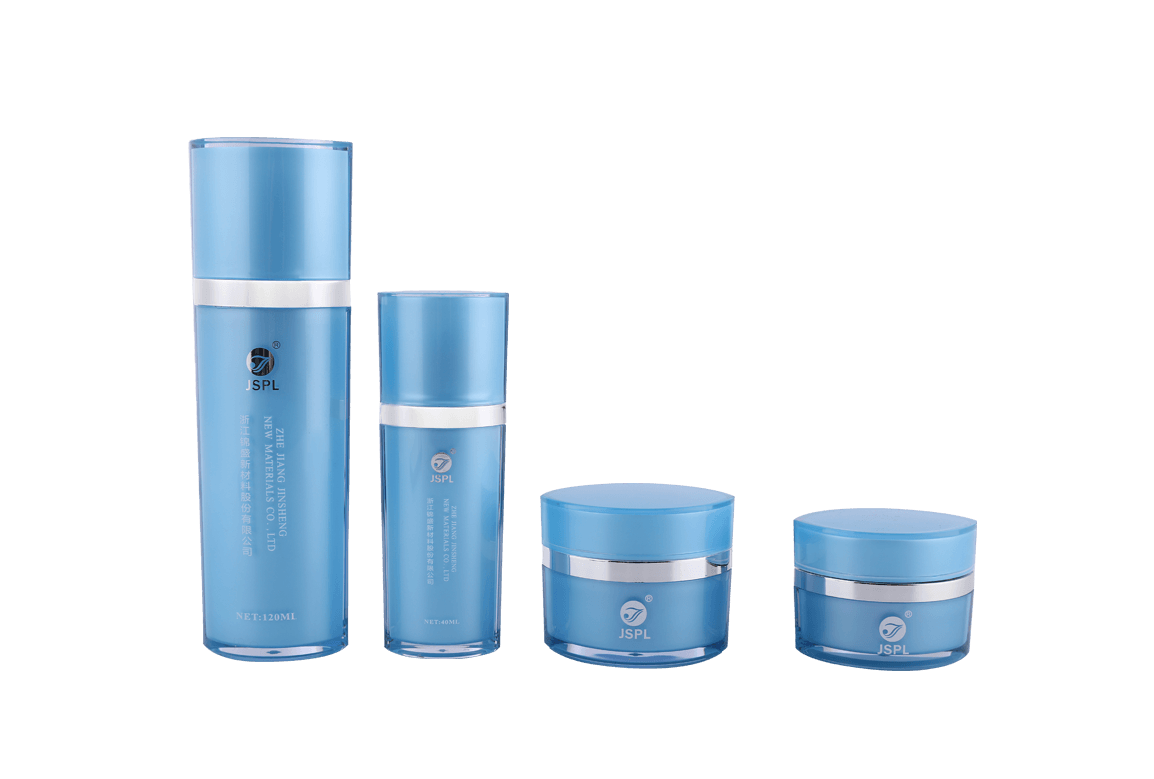
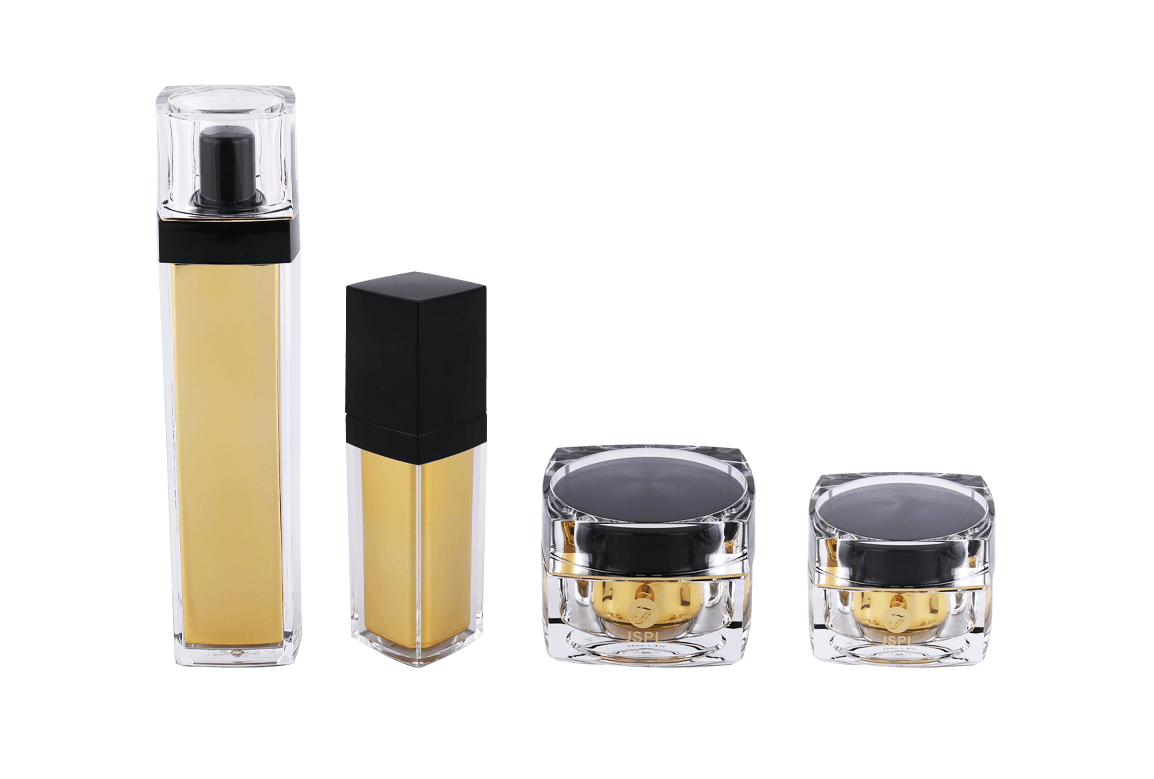
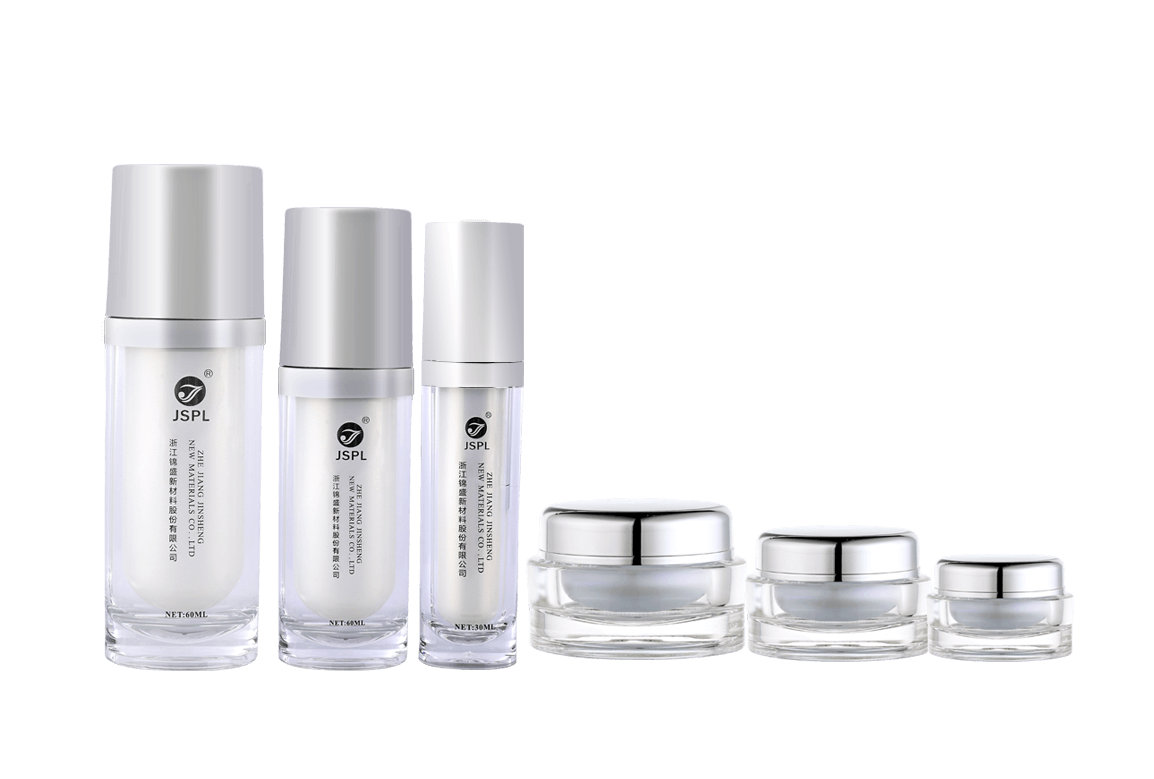
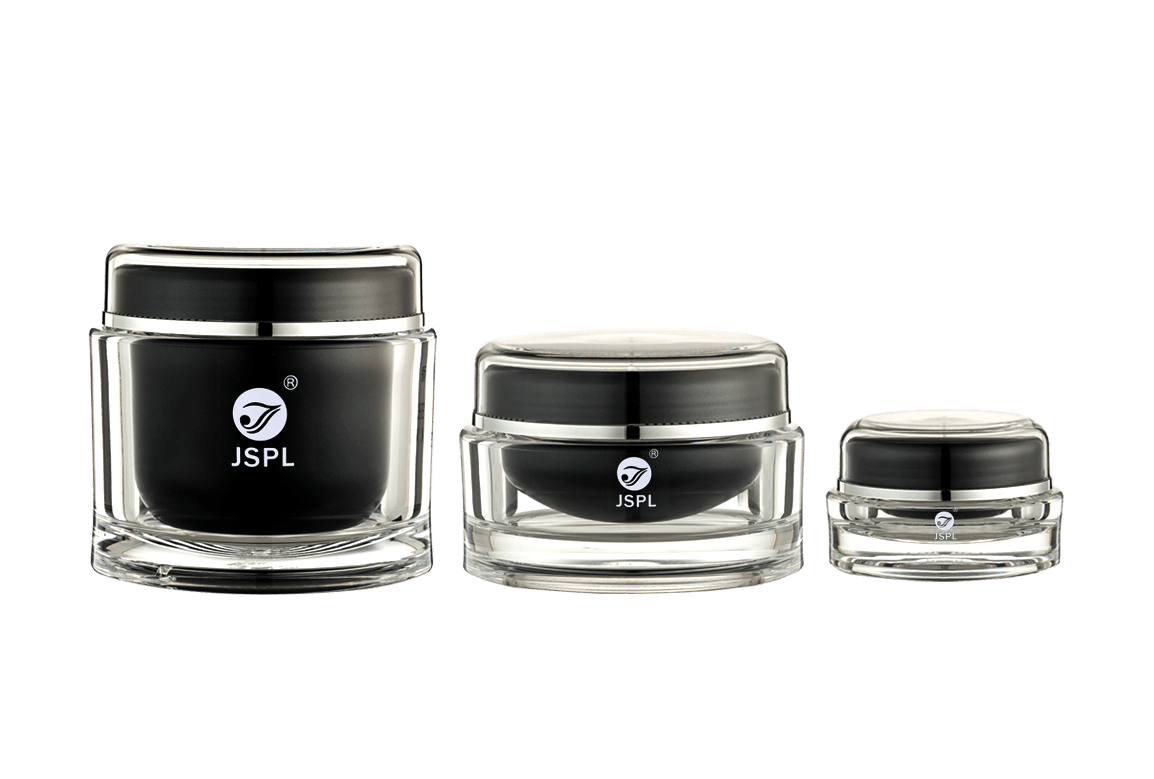
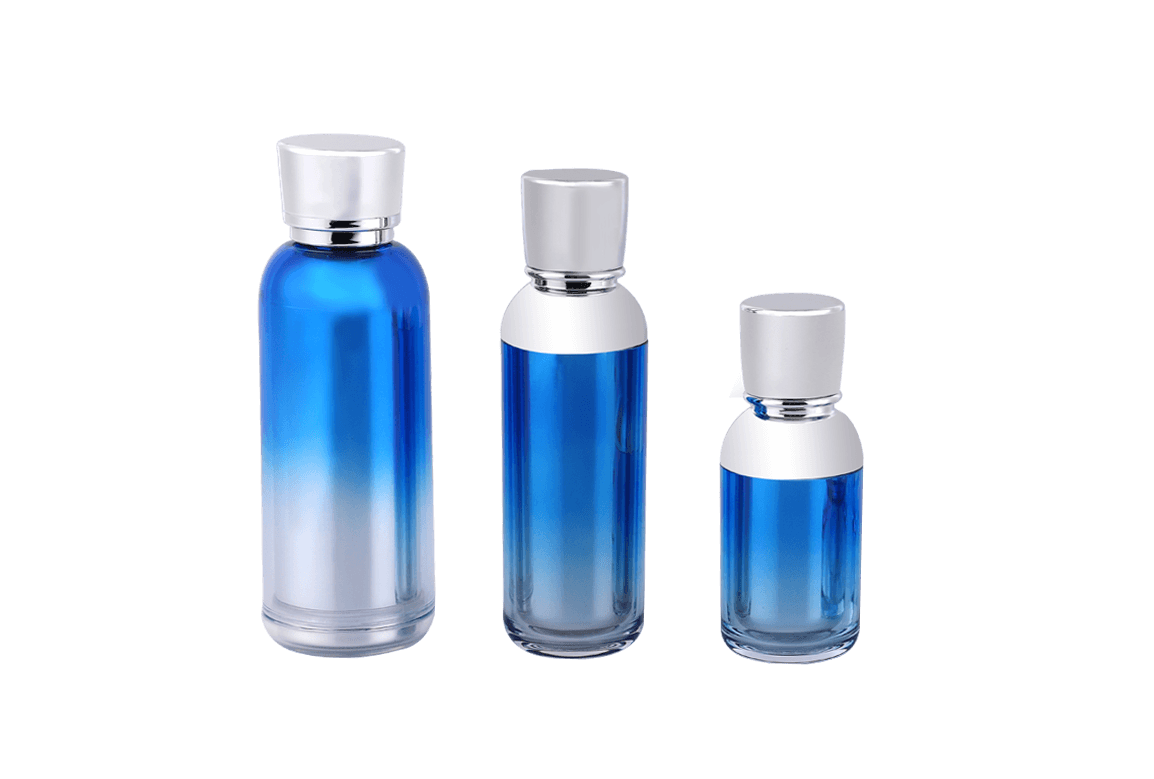
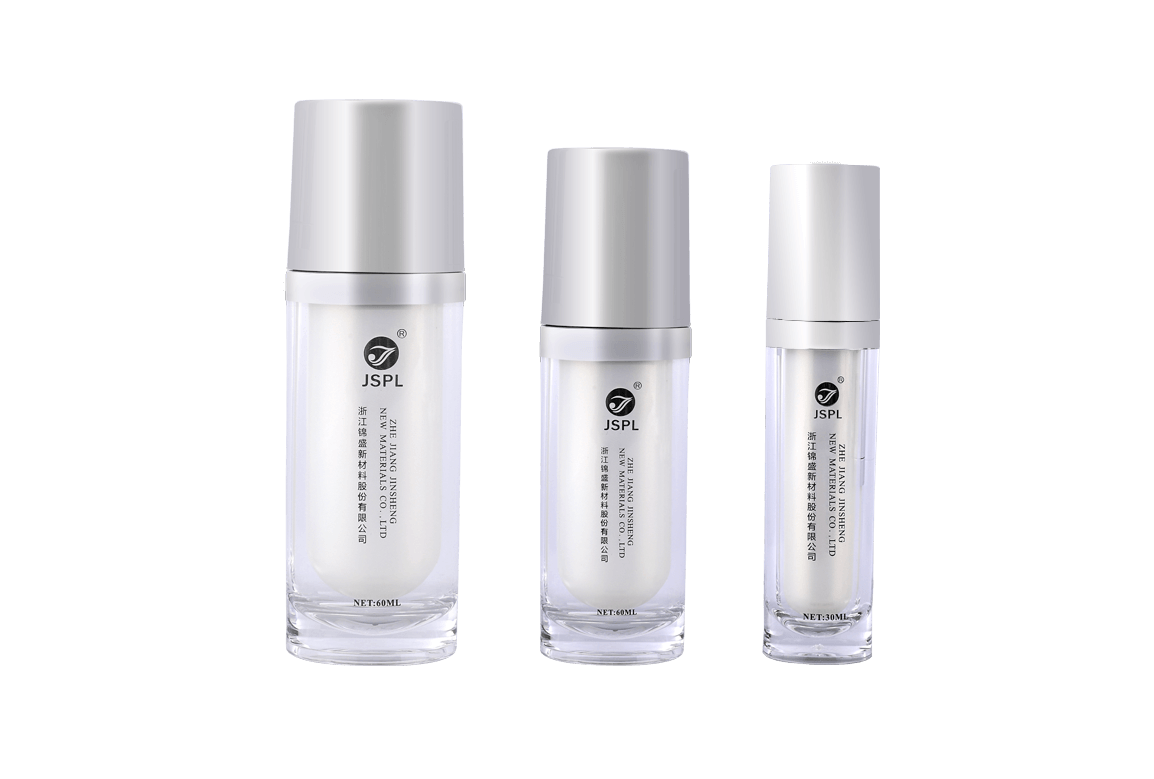
Acrylic (PMMA) is the material of choice for high-end cosmetic containers due to its exceptional optical clarity and crystalline appearance. However, to perfectly capture the properties of PMMA, the design and manufacture of its injection molds must adhere to a series of extremely stringent professional requirements. The mold's precision and surface quality directly determine the final container's smoothness, flawlessness, and premium appearance.
1. Mold Steel and Surface Finishing: The Cornerstone of a Mirror Finish
The "crystal" appearance of acrylic containers demands the highest standards for mold mirror polishing.
High-Grade Mold Steel Selection: Mold steels with excellent polishing properties and high cleanliness, such as vacuum-degassed steels like S136, H13, or P20, must be selected. These steels have minimal internal impurities and can withstand ultra-precision grinding and polishing, providing a solid foundation for achieving optical-grade surface quality.
Optical-Grade Mirror Polish (SPI-A2/A3): Acrylic containers require far higher transparency than standard plastic parts. The mold cavity surface roughness must meet optical-grade standards, typically SPI A2 or higher. This requires multiple stages of hand polishing and diamond polishing using diamond paste or ultra-fine abrasives to ensure the mold cavity is free of micro-scratches and orange peel texture. Any surface imperfections in the mold are directly replicated on the acrylic part.
Coating Protection: To improve the mold's wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and mold release properties, the mold surface is often treated with specialized coatings such as hard chrome or nickel-Teflon. This helps maintain a mirror-like finish over time and prevents minor corrosion that can occur with PMMA at high temperatures.
II. Mold Structure Design: Optimizing Flow and Mold Release
PMMA's high melt viscosity and susceptibility to stress cracking require meticulous mold structure design.
Gating System Design: The selection of gate location and form is crucial, directly impacting both material filling uniformity and the aesthetics of the final product. For acrylic containers requiring high-quality appearance, hot-tip gates or submarine gates are often used. These designs minimize or conceal gate marks, preventing blemishes that affect transparency in the main viewing area.
Runner and runner optimization: The mold runner system should be short and thick to reduce shear heat and flow resistance of the PMMA melt, ensuring stable filling speed and holding pressure. Stagnant flow areas must be avoided to prevent material degradation and black specks.
Mold draft angle and draft angle: Acrylic is highly sensitive to stress concentration. Inadequate draft angles can easily cause drag marks or blushing during ejection, especially on highly polished surfaces. Therefore, a sufficient and uniform draft angle is essential to ensure smooth part demolding.
Wall Thickness Uniformity: To prevent sink marks and warpage, the container's wall thickness should be designed to be as constant as possible. The clearance between the cavity and core must be strictly controlled during mold design to ensure the stability of the product's geometric dimensions and consistent transparency.
III. Precision Temperature Control System: Eliminating Internal Stress and Air Bubbles
Accurate mold temperature control is critical to ensuring the optical quality and mechanical strength of acrylic containers.
Efficient and Balanced Cooling System: Acrylic injection molding requires the mold cavity to be maintained at a relatively high and constant temperature (typically between 60°C and 80°C). The mold must be integrated with a precision temperature control system. When designing the cooling water path, ensure minimal temperature differences across the mold surface to avoid the accumulation of internal stress caused by uneven cooling. Internal stress is the primary cause of cracking, whitening, and light scattering.
Venting System: PMMA is very sensitive to air bubbles and gas traps. The mold must be designed with precise vents to ensure that gas and water vapor within the cavity can be quickly discharged during the melt filling process, preventing the formation of bubbles, splay marks, and other defects that affect transparency.
Drying: Before injection molding, acrylic raw materials must undergo rigorous drying. Mold manufacturers must ensure the cleanliness and humidity control of the entire production environment to prevent injection molding defects.

 Chinese
Chinese España
España Italia
Italia Le français
Le français